A recent C-suite barometer showed a surprising level of optimism among international business leaders. Mark Kennedy deciphers the findings to explain why short-term optimism will need to be buttressed by business transformation plans and long-term investment strategies if organisations are to thrive in a post-pandemic world.
A report detailing over 500 global C-suite leaders’ views on their outlook for 2021 during a worldwide pandemic always had the potential to surprise. Despite the current economic uncertainty, the most surprising finding was the consistent presence of optimism globally, with 71% of respondents assessing the outlook for growth in 2021 as positive.
At the beginning of the pandemic, we witnessed resilience and consistency as some business sectors adapted reasonably quickly. For established companies, there was a kind of ‘muscle memory’ approach to the crisis that unlocked lessons learned and business continuity measures that were initially adopted following the global economic crisis of 2008. Despite the unique nature of the pandemic, businesses that previously invested in crisis management strategies appeared to exhibit more resilience.
The state approach to the pandemic was also a big differentiator, as tax and legislative aid mechanisms created a profoundly different context for business. Countries in Western Europe mostly saw the benefit of this approach. In contrast, other parts of the world, such as Africa, received noticeably less business aid, which resulted in less optimism for the future.
Business transformation plans
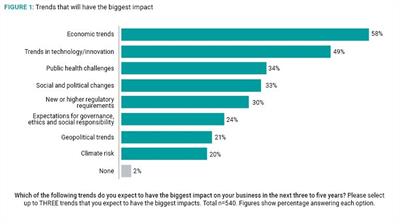
Confidence in managing and mitigating risk during the pandemic was undoubtedly a factor in respondents’ forward-looking business transformation plans. Economic and technology transformation trends scored highly, with 90% expecting to respond to technology and innovation trends and 78% confident in managing upcoming economic trends.
Technology transformation was the most likely focus overall for large companies ($1 billion plus), with 54% of executives indicating a more-than-50% chance of implementing technology transformation plans. While the need to digitally transform businesses has been on the agenda for some time, the crisis appears to have accelerated plans. If we take the retail sector as an example, the need to meet the demand for online shopping during lockdown has added an urgency to prioritising digital strategies.
Perhaps more surprising than what was high on the list of business transformation plans was what respondents considered a low priority. While the travel ban during lockdown highlighted the vast potential to reduce carbon emissions, only 20% of respondents said they expected climate risk to have the most significant impact on their business: the lowest on the list. This figure is slightly higher among Western Europe companies (25%), suggesting it is higher on executive agendas in that region. However, it is less than 20% in Latin America, Africa, Central and Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth Independent States (CEE/CIS), and the US.
One potential reason for climate risk attracting such a low score is the current lack of bottom-line accountability. Despite the growing need to mitigate climate change risk for business sustainability, leaders often treat it as an intangible business issue. They see it as being driven by regulatory momentum rather than a tangible business goal to be approached in the same way as technology or new service transformation plans.
However, climate change will become a matter of profit and loss for many companies over the next ten years, either because it will influence how capital is obtained and the cost of infrastructure, or it will become an opportunity to do more business. It is a similar story with cultural change, which scored equally low on respondents’ business transformation plans. As mandatory reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues becomes more widespread in both cases, businesses will need to consider these developments in business transformation plans.
What is driving the business agenda?
While technological transformation is the overarching theme, how businesses approach plans is often driven by regional and industry factors. In financial services, a high level of regulatory and compliance demands in Western Europe and the US is the driving force for banks and insurance companies launching digital strategies to automate and manage data management and reporting costs. In manufacturing, meanwhile, technology transformation drives improvements in efficiency and productivity.
These regional differences were also evident when looking at investment plan timeframes. Businesses in Africa, for example, are looking at short-term transformation plans to drive profitability. In Europe and Asia, investment plans are put in place as strategic building blocks for the next decade and beyond. While this is not surprising when looking at the maturity of business development in each region, it also reflects the lack of state aid available to prop up economies and businesses in times of crisis.
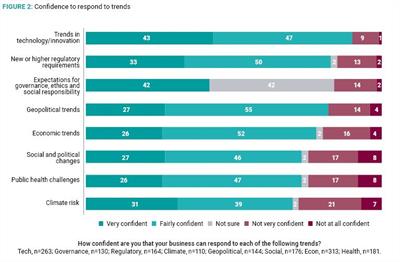
A further factor driving the business agenda is confidence in a company’s ability to respond to trends. In general, the barometer shows that businesses are optimistic in their ability to tackle most trends, with 90% either ‘very’ or ‘fairly’ confident in tackling challenges involving technology and innovation. Businesses in Asia-Pacific are more positive in their ability to respond to technology trends than in Western Europe, with 92% confident there compared to 85% in Western Europe, reflecting the vibrancy of the region’s technology start-up scene.
However, executives are less confident in their businesses’ ability to respond to some other trends. 28% of companies are ‘not very’ or ‘not at all’ hopeful in dealing with the impact of climate change. This lack of confidence in responding to some trends may be down to the fact that, as discussed earlier, it is positioned lower down on the business transformation priority list. A further worrying response is executives’ lack of confidence to deal with social/political changes and public health challenges. While many businesses expect both trends to impact them in the next three to five years, a quarter of respondents are not confident in their ability to address them.
Western European businesses are the least confident in dealing with social/political, climate and public health trends. Less than 65% declared themselves ‘very’ or ‘fairly’ confident for each. Asia-Pacific companies were much more optimistic than their Western European counterparts in responding to public health challenges – 77% of the former looked forward with optimism. This regional difference may reflect Asia-Pacific societies’ longer experience managing epidemics, like the SARS outbreak in 2003.
Longer-term investment strategies
It is important to recognise that the pandemic’s impact on investment plans is critical in moving from a short-term to longer-term outlook. The change in business priorities and how business is conducted since the crisis started has given CEOs across a wide range of sectors a clearer picture of why making long-term and sustainable investments is a sensible business decision. Interestingly, female respondents were more inclined to opt for longer-term investment strategies. Female leaders represent less than one-third of respondents, but with the number of female business leaders rising, the shift to longer-term investment planning is likely to increase. It signals a much-needed focus on long-term business sustainability.
This shift to longer-term sustainability was highlighted by the number of respondents who consider investing in sustainability initiatives to be a relatively long-term business activity. It was rated the fourth longest-term out of 23 activities, behind external growth opportunities, corporate strategy, and research and development (R&D). However, company size and sector had an impact. For manufacturing companies, sustainability initiatives are the longest-term activity of all. This reflects the transition away from fossil fuels and towards more sustainable business models.
Sustainability is seen as a long-term activity in the financial services sector, but sourcing new talent, government engagement, R&D, and maintaining IT systems are higher long-term priorities. It is interesting to note that sourcing new talent is seen as a long-term priority, particularly as the financial services sector is in a phase of disruption driven by technology and new entrants. While this may suggest that the industry sees sourcing new talent as increasingly difficult, it may also hint that financial services companies still see themselves as people industries first and foremost.
The responses from technology and telecoms companies indicate that sustainability initiatives are viewed as one of the shortest-term activities in those sectors. External growth opportunities and regulatory issues are the two longest-term categories for this group, which considers acquiring customers as a longer-term activity than maintaining customers. It paints a picture of an industry that sees high growth as the key to its long-term and short-term future and one that is less concerned about its physical footprint and managing long-term external risks when compared to other, older industries. Of course, as new EU privacy laws become even more embedded, the technology sector may see regulation as both a short-term and long-term priority.
Company size is a further factor. Larger ($1 billion plus) companies are most likely to consider sustainability as a longer-term business activity, reflecting that they have the resources to build a sustainability programme and the more significant external pressure on large and recognisable businesses to address sustainability issues. Executives from small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) still regard sustainability as a relatively long-term activity, but R&D, corporate strategy, and external growth are viewed as higher long-term priorities.
Framing a reset strategy
What can we learn from the barometer results, and does it help frame strategies as companies look to reset? Looking at differences as well as similarities can give CEOs some bell-weather trends to consider. Take the fact that the barometer portrays businesses as generally optimistic. This helps provide momentum and confidence for the growth outlook, even though executives will consider different growth strategies and action pathways. It is then a question of looking at that growth landscape in more detail, so plans are more robust.
Another key takeaway from the barometer is that businesses across the spectrum are prioritising driving technological change in one form or another. This could be implementing technology to transform and improve productivity, reduce costs, capture a business advantage from, say, increased online demand for products and services, or using it to enrich and enhance marketing strategies. Again, it is about capitalising on specific trends within the business sector. One aspect of technological change to keep in focus is the need to mitigate risk. With increasing complexity in the data and privacy regulatory landscape, it is crucial that – similar to technology transformation plans – risk mitigation remains high on CEOs’ agendas.
With the barometer also highlighting a growing appetite for ESG themes, it is essential to keep track of sustainability issues – particularly when reporting. ESG reporting is still not a high enough priority for CEOs, but it will demand greater focus from a risk management perspective in the future. Also not to be overlooked is the opportunity for businesses to create strategic business advantage by becoming an early adopter of, for example, environmentally friendly solutions or applying ESG as a business differentiator.
Finally, a more oblique takeaway from the barometer’s high level of business optimism was the importance of investing in resilience. As we saw from government and company reaction at the beginning of the pandemic, lessons of the last economic crisis appeared to have been learned, particularly on the importance of continuity and making businesses more resilient to shocks. There are many examples of companies achieving business continuity success, whether through the ability to add flexibility in the supply chain or rapidly adapt products to meet changing consumer and business needs.
It is clear that, where CEOs take the time to fully understand business and regulatory trends and invest in forward-looking strategies such as resilience and sustainability, charting a course out of the crisis will not be driven by short-term optimism alone but a realistic long-term growth strategy.
Mark Kennedy is Managing Partner at Mazars in Ireland.
 LOADING...
LOADING...