Recent proposals from the International Accounting Standards Board could have dramatic effects on how companies present their financial performance.
By Terry O’Rourke and Barbara McCormack
When Gary Kabureck, a board member of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), presented an update on IFRS developments in Chartered Accountants House last October, he alerted us to the impending proposals from the IASB on how companies’ financial performance should be presented in the profit and loss account (or to use the IFRS term, the ‘statement of profit or loss’). Sure enough, just before Christmas, the IASB issued a 200-page Exposure Draft proposing substantial changes in response to demands from users for better information on financial performance, which would reduce the diversity of presentation and enhance comparability between companies.
At a high level, the profit and loss account would be required to classify income and expenses into the following categories: operating, investing, financing, associates and joint ventures, income tax, and discontinued operations. However, the level of prescription and definition underpinning the presentation of income and expenses in these categories is quite detailed and could cause significant changes in how companies present their results.
Operating profit
A key proposal is that the operating category, which is intended to include all income and expenses from the main business activities, would be the default category, to include all income and expenses that are not defined in one of the other categories. This would include items such as restructuring costs and goodwill impairments, irrespective of whether they are regarded by management as once-off or exceptional. The resultant operating profit or loss would be presented on the face of the profit and loss account. While many companies currently choose to present operating profit, its composition may well be different under these proposals.
For example, associates and joint ventures would be split into those that are integral to the entity’s operations and those that are not. The results from those that are integral would be presented as a separate line item after operating profit while those that are not integral would be included in the investing category. The investing category would also include returns, and related expense, from other investments that are generated individually and largely independently of the entity’s other resources.
Prohibiting the use of columns
Many Irish and UK companies make use of columns on the face of the profit and loss account to present adjusted profit measures such as operating profit before exceptional restructuring or impairment expense.
The proposals in the Exposure Draft include a prohibition on the use of columns to present management performance measures in the profit and loss account. The proposed definition of management performance measures would likely include such adjusted profit measures and they would therefore be prohibited from being presented in columnar format on the face of the profit and loss account. The Exposure Draft notes that “a few entities use a columnar approach” to present management performance measures based on a sample of 100 large companies from around the world. However, had the sample been taken from Ireland and the UK, it may well have shown a much greater incidence of columnar reporting. The IASB notes that the prohibition would be a change for some companies “operating in jurisdictions where the use of columns is common”.
It will be interesting to see if stakeholders request further clarity from the IASB on what, if any, types of measures can be included in columnar format in the profit and loss account.
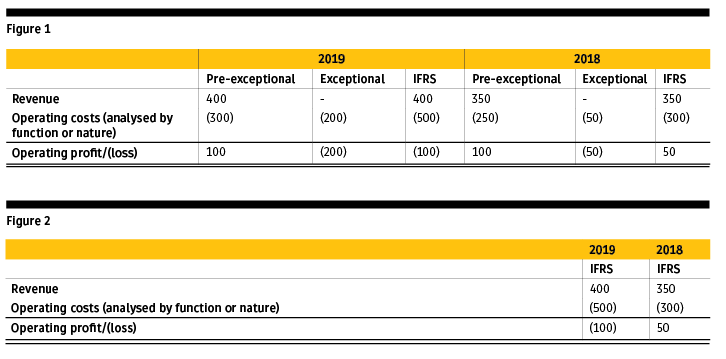
Figure 1 shows what an extract from the face of a profit and loss account using columns to strip out exceptional items might look like, while Figure 2 shows the numbers without columns. There will undoubtedly be companies who consider that the columnar format in Figure 1 provides more useful information about their performance, particularly in relation to the year-on-year comparison.
It is notable that if the Brexit transition period ends on 31 December 2020, it will be for a newly established UK IFRS Endorsement Board to decide whether to adopt new IFRS standards in the UK having consulted with UK stakeholders. Consequently, if the IASB proceeds to include its current proposals in the final IFRS and the EU adopts that Standard, perhaps during 2021, there is no guarantee that UK listed companies will have to comply with all the requirements of the eventual IFRS Standard.
The Exposure Draft proposes that, where a company uses management performance measures to communicate with users, those measures should be included in a note to the financial statements with a reconciliation to the most directly comparable IFRS number, and other information including an explanation as to why those measures are useful. Because EBITDA is a commonly used measure in communications with users, the IASB considered defining EBITDA. But it is instead proposing that operating profit or loss before depreciation and amortisation would be specified as not being a management performance measure and therefore, would not need the above-noted reconciliation and explanation.
The Exposure Draft proposes to continue to permit the inclusion of adjusted earnings per share measures in the notes to the financial statements, with appropriate explanation and reconciliation. However, it proposes that such measures would not be permitted to be presented on the face of the profit and loss account.
Unusual income and expense
The Exposure Draft proposes to define unusual income and expenses as those with “limited predictive value” and that this is the case “when it is reasonable to expect that income or expenses that are similar in type and amount will not arise for several future annual reporting periods”. The amount and nature of items of unusual income and expense would be set out in a single note to the financial statements.
The proposed definition of unusual items, with its focus on predictive value, may cause some companies to change their assessment of what unusual items need to be disclosed.
Analysis of expenses
The Exposure Draft proposes that operating expenses would be analysed in the profit and loss account using either the nature of expense method (e.g. raw materials, employee benefits, depreciation) or the function of expense method (e.g. cost of sales, administrative expenses). However, companies would not have a free choice of which method to use. They would have to assess which method provides the most useful information to users by reference to a number of considerations set out in the Exposure Draft. Using a mixture of the two methods would be specifically prohibited, with very limited exceptions. Where the function of expense method is used in the profit and loss account, an analysis of total operating expenses by nature would be required in the notes, with new criteria designed to curtail the amount labelled “other”.
A number of companies that highlight the effect of exceptional items by including line items or sub-totals, rather than columns, in the profit and loss account would have to be careful to comply with the proposed more prescriptive rules on the layout and content of the profit and loss account.
Other proposals
The Exposure Draft is titled General Presentation and Disclosures, and is intended to replace IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements. Although the 200-page Exposure Draft makes a number of proposals in relation to the statement of financial position, the statement presenting comprehensive income, the statement of cash flows and the notes to the financial statements, as well as related changes to other IFRS standards, we have sought in this article to focus principally on some of the key proposals that would affect how the profit and loss account is presented by many Irish listed companies. The IASB has set 30 June 2020 as the date by which it requires comments on the proposals in the Exposure Draft.
The IASB has included illustrative examples in the Exposure Draft to show how its proposals should be used by banking, insurance, and property investment companies.
Practical implications
The IASB notes that, although the proposals do not affect the recognition or measurement of assets, liabilities, income, or expense, they would have a number of practical implications that would give rise to additional costs for preparers. Examples of costs that may arise include the cost of process or system changes necessary to identify and capture the various types of income and expenses to be separated and disclosed, training costs for staff, and the costs of communicating the reporting consequences to stakeholders. The effect on covenants in banking and loan agreements may also need to be considered. Nonetheless, the IASB considers that the changes are desirable in order to respond to the demands of users and it notes specifically the benefits for the quality of electronic reporting, including comparability and consistency.
Conclusion
It is notable that the IASB has issued an Exposure Draft, rather than a Discussion Paper, indicating it has reached an advanced stage of confidence that its proposals should be implemented. It will be interesting to see the level of support or otherwise the IASB receives on its proposals from companies, investors, and other stakeholders. Given the scale of the changes proposed in the Exposure Draft, we can expect the reaction of the board of the IASB to comments to be closely monitored by companies whose reporting would be significantly affected, and by investors whose demands and expectations the IASB is endeavouring to meet.
Terry O’Rourke FCA is Chair of the Accounting Committee at Chartered Accountants Ireland.
Barbara McCormack FCA is Technical Manager, Advocacy and Voice, at Chartered Accountants Ireland.
 LOADING...
LOADING...